Abstract
Objective:
To assess the relationship between early laboratory parameters, disease severity, type of management (surgical or conservative) and outcome in necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
Study design:
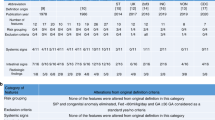
Retrospective collection and analysis of data from infants treated in a single tertiary care center (1980 to 2002). Data were collected on disease severity (Bell stage), birth weight (BW), gestational age (GA) and pre-intervention laboratory parameters (leukocyte and platelet counts, hemoglobin, lactate, C-reactive protein).
Results:
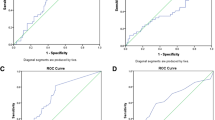
Data from 128 infants were sufficient for analysis. Factors significantly associated with survival were Bell stage (P<0.05), lactate (P<0.05), BW and GA (P<0.01, P<0.001, respectively). From receiver operating characteristics curves, the highest predictive value resulted from a score with 0 to 8 points combining BW, Bell stage, lactate and platelet count (P<0.001). At a cutoff level of 4.5 sensitivity and specificity for predicting survival were 0.71 and 0.72, respectively.
Conclusion:
Some single parameters were associated with poor outcome in NEC. Optimal risk stratification was achieved by combining several parameters in a score.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guthrie S, Gordon P, Thomas V, Thorp J, Peabody J, Clark R . Necrotizing enterocolitis among neonates in the United States. J Perinatol 2003; 23: 278–285.
Llanos A, Moss M, Pinzon M, Dye T, Sinkin R, Kendig J . Epidemiology of neonatal necrotizing entrocolitis: a population-based study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2002; 16: 342–349.
Hutter J, Hathaway W, Wayne E . Hematologic abnormalities in severe neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 1976; 88: 1026–1031.
Ververidis M, Kiely E, Spitz L, Drake D, Eaton S, Pierro A . The clinical significance of thrombocytopenia in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 2001; 36: 799–803.
Pourcyrous M, Korones SB, Yang W, Boulden TF, Bada HS . C-reactive protein in the diagnosis, management, and prognosis of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics 2005; 116 (5): 1064–1069.
Malik A, Hui CP, Pennie RA, Kirpalani H . Beyond the complete blood cell count and C-reactive protein: a systematic review of modern diagnostic tests for neonatal sepsis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2003; 157 (6): 511–516.
Caplan MS, Kelly A, Hsueh W . Endotoxin and hypoxia-induced intestinal necrosis in rats: the role of platelet activating factor. Pediatr Res 1992; 31 (5): 428–434.
Backstrom T, Liska J, Oldner A, Lockowandt U, Franco-Cereceda A . Splanchnic metabolism during gut ischemia and short-term endotoxin and hemorrhagic shock as evaluated by intravasal microdialysis. Shock 2004; 21 (6): 572–578.
Abubacker M, Yoxall CW, Lamont G . Peri-operative blood lactate concentrations in pre-term babies with necrotising enterocolitis. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2003; 13 (1): 35–39.
Garcia J, Smith FR, Cucinell SA . Urinary D-lactate excretion in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 1984; 104 (2): 268–270.
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 1978; 187 (1): 1–7.
Kling P, Hutter J . Hematologic abnormalities in severe neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: 25 years later. J Perinatol 2003; 23: 523–530.
Schober PH, Nassiri J . Risk factors and severity indices in necrotizing enterocolitis. Acta Paediatr 1994; 396 (Suppl): 49–52.
Voss M, Moore S, van der Merwe I, Pieper C . Fulminating necrotising enterocolitis: outcome and prognostic factors. Pediatr Surg Int 1998; 13: 576–580.
Camberos A, Patel K, Applebaum H . Laparotomy in very small premature infants with necrotizing enterocolitis or focal intestinal perforation: Postoperative outcome. J Pediatr Surg 2002; 12: 1692–1695.
Kenton AB, O'Donovan D, Cass DL, Helmrath MA, Smith EO, Fernandes CJ et al. Severe thrombocytopenia predicts outcome in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Perinatol 2005; 25 (1): 14–20.
Ragazzi S, Pierro A, Peters M, Fasoli L, Eaton S . Early full blood count and severity of disease in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Surg Int 2003; 19: 376–379.
Lange H, Jackel R . Usefulness of plasma lactate concentration in the diagnosis of acute abdominal disease. Eur J Surg 1994; 160 (6–7): 381–384.
Murray MJ, Gonze MD, Nowak LR, Cobb CF . Serum D(−)-lactate levels as an aid to diagnosing acute intestinal ischemia. Am J Surg 1994; 167 (6): 575–578.
Murray MJ, Barbose JJ, Cobb CF . Serum D(−)-lactate levels as a predictor of acute intestinal ischemia in a rat model. J Surg Res 1993; 54 (5): 507–509.
Gunel E, Caglayan O, Caglayan F . Serum D-lactate levels as a predictor of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pediatr Surg Int 1998; 14 (1–2): 59–61.
Gupta S, Burke G, Herson V . Necrotizing enterocolitis: laboratory indicators of surgical disease. J Pediatr Surg 1994; 29: 1472–1475.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Dr F Zepp, Chairman of the Department of Pediatrics at the Johannes Gutenberg-University in Mainz, Germany for providing access to the ICU patient's records, and the DAAD (German Academic Exchange Office) for supporting Dr A Mungnirandr from Bangkok, Thailand for this scientific project during his clinical fellowship in Mainz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kessler, U., Mungnirandr, A., Nelle, M. et al. A simple presurgical necrotizing enterocolitis-mortality scoring system. J Perinatol 26, 764–768 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211613
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211613
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Risk factors for mortality in preterm infants with necrotizing enterocolitis: a retrospective multicenter analysis
European Journal of Pediatrics (2022)
-
Postoperative sepsis in infants below 6 months of age
World Journal of Pediatrics (2009)