Abstract
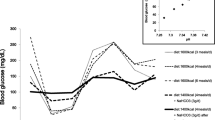
We report on two children with mild persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. In both, oral nifedipine treatment (0.7 and 2.0 mg/kg per day respectively) had a significant clinical effect. In one case, nifedipine monotherapy prevented hypoglycaemia; in the second case, the dosage and the side-effects of other substances could be reduced, thus circumventing surgical therapy.
Conclusion Nifedipine treatment has a favourable effect on the clinical course of patients with mild hyperinsulinism. It represents a valuable new substance for the treatment of this disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 March 1998 / Accepted: 3 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eichmann, D., Hufnagel, M., Quick, P. et al. Treatment of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia with nifedipine. Eur J Pediatr 158, 204–206 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310051049
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310051049