Abstract
Abstract
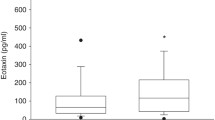
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease often occurring in ventilator-treated very low birth weight infants. The aetiology of BPD is multifactorial and pulmonary immaturity, high oxygen concentrations, peak inspiratory pressure levels and large tidal volumes during prolonged mechanical ventilation are important factors. We measured in tracheobronchial aspirate fluid (TAF) the concentrations of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor α, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1 receptor antagonist in infants requiring artificial ventilation for BPD (n=17) or respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) (n=15) or postoperatively after surgery (n=15). The median levels of all studied cytokines in TAF were higher in infants with BPD without local or systemic corticosteroid, treatment compared to the median TAF levels of BPD neonates treated with corticosteroids (P=0.06−P<0.01). The neonates with BPD not treated with corticosteroids also showed higher levels of the five studied cytokines in TAF compared to infants on short-time ventilator treatment (P<0.01−P<0.001) and compared to neonates with RDS (P=0.07−P<0.001). The corticosteroid treated neonates with BPD had TAF cytokine levels approaching those of the control neonates.
Conclusion
Tumour necrosis factors α, IL-1β, IL6, IL8 and IL 1 ra were markedly elevated in tracheobronchial aspirate fluids from neonates with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Corticoid treatment seemed to reduce these levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPD :
-
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- IL-1 :
-
interleukin-1
- IL-1ra :
-
interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
- IL-6 :
-
interleukin-6
- IL-8 :
-
interleukin-8
- PMNL :
-
polymorphonuclear leucocytes
- RDS :
-
respiratory distress syndrome
- TAF :
-
tracheobronchial aspirate fluid
- TNF :
-
tumour necrosis factor
References
Arend WP (1991) Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. A new member of the interleukin 1 family. J Clin Invest 88: 1445–1451
Bancalari E, Abdenour GE Feller R, Gannon J (1979) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical presentation. J Pediatr 95:819–823
Cassell GH, Crouse DT, Canupp KC, et al (1988) Association ofUreaplasma urealyticum infection of the lower respiratory tract with chronic lung disease and death, in very-low-birth-weight infants. Lancet II:240–245
Clement A, Chadelat K, Sardet A, Grimfeld A, Tournier G (1988) Alveolar macrophage status in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res 23: 470–473
Cummings JJ, D'Eugenio DB, Gross SJ (1989) A controlled trial of dexamethasone in preterm infants at high risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med 320.:1505–1510
D'Ablang G, Bernard B, Zaharov I, Barton L, Kaplan B, Schwinn CP (1975) Neonatal pulmonary cytology and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Acta Cytol 19:21–27
Dinarello CA (1991) The proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor and treatment of the septic shock syndrome. J. Infect Dis 163:1177–1184
Dinarello CA, Wolff SM (1993) The role of interleukin-1 in disease. N Engl J Med 328:106–113
Donnelly SC, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, et al (1993) Interleukin-8 and development of respiratory distress syndrome in at-risk patient groups. Lancet 341: 643–647
Gerdes JS, Harris MC, Polin RA (1988) Effects of dexamethasone and indomethacin on elastase, α2-proteinase inhibitor, and fibronectin in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from neonates. J Pediatr 113:727–773
Giedion A, Haefliger H, Dangel P (1973) Acute pulmonary X-ray changes in hyaline membrane disease treated with artificial ventilation and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). Pediatr Radiol 1:145–152
Grigg JM, Barber A, Silverman M (1991) Increased levels of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid interleukin-6 in preterm ventilated infants after prolonged rupture of membranes. Am Rev Respir Dis 145:782–786
Groneck P, Speer CP (1993) Interleukin-8 in pulmonary efflnent fluid of preterm infants. J Pediatr 123:839–840
Jorens PG, Richmaneisenstat JBY, Housset BP, et al (1992) Interleukin-8 induces neutrophil accumulation but not protease secretion in the canine trachea. Am J Physiol 6:L708–713
Knowles MR, Church NL, Waltner WE, et al (1990) A pilot study of aerolized amiloride for the treatment of lung disease in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med 322:1189–1194
LaForce WR, Brudno DS (1993) Controlled trial of beclomethasone dipropionate by nebulization in oxygen- and ventilator-dependent infants. J Pediatr 122:285–288
Mammel MC, Johnson DE., Green TP, Thompson TR (1983) Controlled trial of dexamethasone therapy in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lancet I:1356–1358
McColm JR, McIntosh N (1994) Interleukin-8 in bronchoalveolar lavage samples as a predictor of chronic lung disease in premature infants. Lancet 343:729
Merritt TA, Stuard ID, Puccia J, et al (1981) Newborn tracheal aspirate cytology: Classification during respiratory distress syndrome and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr 98: 949–956
Merritt TA, Puccia JM, Stuard ID (1981) Cytologic evaluation of pulmonary effluent in neonates with respiratory distress syndrome and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Acta Cytol 25: 631–639
Merritt TA, Cochrane CG, Holcomb K, et al (1983) Elastase and α2-proteinase inhibitor activity in tracheal aspirates during respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest 72:656–666
Millar AB, Singer M, Meager A, Foley NM, Johnson NMcI, Rook GAW (1989) Tumour necrosis factor in bronchopulmonary secretions of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet II:712–714
Miller EJ, Cohen AB, Nagao S, et al (1992) Elevated levels of NAP-1/interleukin-8 are present in the airspaces of patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome and are associated with increased mortality. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:427–432
Murch SH, MacDonald TT, Wood CBS, Costeloe KL (1992) Tumour necrosis factor in the bronchoalveolar secretions of infants with the respiratory distress syndrome and the effect of dexamethasone treatment. Thorax 47: 44–47
Ng PC (1993) The effectiveness and side effects of dexamethasone in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Arch Dis Child 68: 330–336
Noack G, Mortensson W, Robertson B, Nilsson R (1993) Correlations between radiological and cytological findings in early development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur J Pediatr 152: 1024–1029
Northway WH (1990) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: then and now. Arch Dis Child 65:1076–1081
Northway WH, Rosan RC, Porte DY (1967) Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. N. Engl J Med 276:357–368
Ohlsson K, Björk P, Bergenfeldt M, Hageman R Thompson RC (1990) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature 348:550–552
Philip AGS (1975) Oxygen plus pressure plus time: the etiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 55: 44–50
Rolfe MW, Kunkel SL, Rowens B, Standiford TJ, Cragoe EJ, Strieter RM (1992) Suppression of human alveolar macrophage-derived cytokines by amiloride. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 6:576–582
Rosenfeld W, Evans H, Concepcion L, Jhaveri R, Schaeffer H, Friedman A (1984) Prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia by administration of bovine superoxide dismutase in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr 105:781–788
Schröder JM (1992) Interleukin 8. Advances Neuroimmunol 2: 109–124
Snick van J (1990) Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol 8:253–278
Southall DP, Samuels MP (1990) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a new look at management. Arch Dis Child 65:1089–1095
Suter PM, Suter S, Girardin E, Roux-Lombard P, Grau GE, Dayer J-M (1992) High bronchoalveolar levels of tumor necrosis factor and its inhibitors, interleukin-1, interferon, and elastase, in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome after trauma, shock, or sepsis. Am Rev Respir Dis 145:1016–1022
Svenningsen NW (1984) Clinical criteria of RDS. In: Raivio KO, Hallman N, Kouvalainen K (eds) Respiratory distress syndrome. Academic Press, London, pp 133–145
Wakabayashi G, Gelfand JA, Burke JF, Thompson RC, Dinarello CA (1991) A specific receptor antagonist for interleukin 1 preventsEscherichia coli-induced shock in rabbits. FASEB J 5: 338–343
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tullus, K., Noack, G.W., Burman, L.G. et al. Elevated cytokine levels in tracheobronchial aspirate fluids from ventilator treated neonates with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur J Pediatr 155, 112–116 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02075762
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02075762