Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of infusion of dopexamine hydrochloride, a new synthetic catecholamine, on cardiopulmonary status and urine output in neonates with respiratory and circulatory failure.
Design
Prospective clinical study with each patient serving as his own control.
Setting
Intensive care unit (14 beds) in a 300-bed paediatric teaching hospital.
Patients
Seventeen neonates with low birth weight (LBW) requiring mechanical ventilation in the first 4 days of life, who initially had two of the following symptoms: hypotension, oliguria, metabolic acidosis with base deficit >10 and failure to respond to volume loading.
Interventions
Cardiopulmonary variables, diuresis and acid-base status were measured before and after volume loading, in patients who did not improve infusion of dopexamine was started at a dose of 2μg kg−1 min−1 which was titrated to achieve blood pressure, urine output, and base deficit in normal range. Observations were continued for a period of 5 h.
Measurements and results
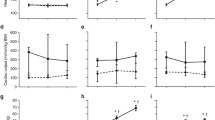
Systolic blood pressure increased significantly after 3 h. of dopexamine infusion and remained elevated up to the end of the study period. Diastolic and mean blood pressure increased slightly (NS). Diuresis increased significantly from the 4th h of dopexamine infusion. Arterial blood pH increased significantly from baseline at 5 h after the start of dopexamine administration. There was also a significant imporovement in the PtcO2/PaO2 index.
Conclusion
In neonates with respiratory and circulatory failure, dopexamine increases blood pressure and improves arterial pH and urine output.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cuevas L, Yeh TF, John EG, Cuevas D, Plides RS (1991) The effect of low-dose dopamine infusion on cardiopulmonary and renal status in premature newborns with respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Dis Child 145: 799–803
DiSessa TG, Leitner M, Ti CC, Gluck L, Coen R, Friedman WF (1981) The cardiovascular effects of dopmamine in the severely asphyxiated neonate. J Pediatr 99: 772–776
Gill AB, Weindling AM (1993) Randomised controlled trial of plasma protein fraction versus dopamine in hypotensive, very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child 69: 284–287
Greenough A, Emery EF (1993) Randomized trial comparing dopmaine and dobutamine in preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr 152: 925–927
Miall-Allen VM, Whitelaw AGL (1989) Response to dopamine and dobutamine in preterm infants of less than 30 weeks gestation. Crit Care Med 17: 1166–1169
Padbury JF, Agata Y, Baylen BG, Ludlow JK, Polk DH, Goldblatt E, Pescetti J (1986) Dopamine pharmacokinetics in critically ill newborn infants. J Pediatr 110: 293–298
Perez CA, Reimer JM, Schreiber MD, Warburton D, Gregory GA (1986) Effect of high-dose dopamine on urine output in newborn infants. Crit Care Med 14: 1045–1049
Seri I, Tulassay T, Kiszel J, Machay T, Csmor S (1984) Cardiovascular response to dopamine in hypotensive preterm neonates with severe hyaline membrane diseases. Eur J Pediatr 142: 3–9
Gill AB, Weindling AM (1992) Echocardiographic assessment of cardiac function in shocked very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child 68: 17–21
Emery EF, Greenough A (1993) Efficacy of low-dose dopamine infusion. Acta Paediatr 82: 430–432
Molloy WD, Dobson K, Girling L, Greenberg ID, Prewitt RM (1984) Effects of dopamine on cardiopulmonary function and left ventricular volumes in patients with acute respiratory failure. Am Rev Respir Dis 130: 396–399
Molloy DW, Ducas J, Dobson K, Girling L, Prewitt RM (1986) Hemodynamic management in clinical acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Dopamine versus dobutamine. Chest 89: 636–640
Prewitt RM, McCarthy J, Wood LDH (1981) Treatment of acute low-pressure pulmonary edema in dogs. J Clin Invest 67: 409–418
Westman L, Jamberg PO (1986) Effects of dobutamine on renal function in normal man. Acta Anaethesiol Scand 30: 72–75
Rozé JC, Tohier C, Maingueneau C, Lefevre M, Mouzard A (1993) Response to dobutamine and dopamine in the hypotensive, very preterm infant. Arch Dis Child 69: 59–63
Brown RA, Dickson J, Farmer JB, Hall JC, Humphries RG, Ince F, O'Connor SE, Simpson WT, Smith GW (1985) Dopexamine: a novel agonist at peripheral dopamine and beta 2 adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol 85: 599–608
Magrini F, Foulds R, Roberts N, Macchi G, Mondadori C, Zanchetti A (1987) Human renovascular effects of dopexamine hydrochloride: a novel agonist of peripheral dopamine and beta 2 adrenoreceptors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 32: 1–4
Smith GW, Hall JC, Farmer JB, Simpson WT (1987), The cardiovascular actions of dopexamine hydrochloride, an agonist at dopamine receptors and beta-2 adrenoceptors in the dog. J Pharm Pharmacol 39: 636–641
Jaski BE, Wijns W, Foulds R, Serruys PW (1986) The haemodynamic and myocardial effects of dopexamine: a new beta-2 adrenoceptor and dopaminergic agonist. Br J Clin Pharmacol 21: 393–400
Hunter DN, Gray H, Mudaliar Y, Morgan C, Evans TW (1989) The effects of dopexamine hydrochloride on cardiopulmonary haemodynamics following cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Int J Cardiol 23: 365–371
Bayliss J, Thomas L, Poole-Wilson P (1987) Acute hemodynamic and neuroendocrine effects of dopexamine, a new vasodilator for the treatment of heart, failure: comparison with dobutamine, captopril and nitrate. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9: 551–554
Svensson G, Sjogren A, Erhardt L (1986) Short-term haemodynamic effects of dopexamine in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Eur Heart J 7: 697–703
Baumann G, Gutting M, Pfafferott C, Ningel K, Klein G (1988) Comparison of acute haemodynamic effects of dopexamine hydrochloride, dobutamine and sodium nitroprusside in chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 9: 503–512
Tan L-B, Littler WA, Murray, RG (1987) Beneficial haemodynamic effects of intravenous dopexamine in patients with low-output heart failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 10: 280–286
Bodenham AR, Park GR (1988) Dopexamine hydrochloride, a novel drug with renal, vasodilator properties: two case studies. Intensive Care Med 14: 663–665
Olsen NV, Lund J, Jensen PF, Espersen K, Kanstrup I-L, Plum I, Leyssac PP (1993) Dopamine, Dobutamine, and Dopexamine. A comparison of renal effects in unanesthetized human volunteers. Anesthesiology 79: 685–694
Taylor BJ, Rogers BW, Sziszak TL, Sziszak TJ (1993) Effects of dopexamine on hemodynamics and oxygen consumption after beta blockade in lambs. Crit Care Med 21: 733–739
Versmold HT, Kitterman JA, Phibbs RH, Gregory GA, Tooley WH (1981) Aortic blood pressure during the first 12 hours of life in infants with birth weigth 610 to 4222 grams. Pediatrics 67: 607–613
Weindling AM (1989) Blood pressure monitoring in the newborn. Arch Dis Child 64: 444–447
Morley CJ (1986) The respiratory distress syndrome. In: Roberton NRC (ed) Textbook of neonatology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Lund N, de Asila RJ, Papadakos PJ, Thorborg PAJ (1992) Dopexamine hydrochloride in septicemia: effects on gut, liver and muscle oxygenation. Crit Care Med 20: S46
Dawson JR, Thompson DS, Signy M, Juul SM, Turnbull P, Jenkins BS, Webb-Peploe MM (1985) Acute haemodynamic and metabolic effects of dopexamine, a new dopaminergic receptor agonist, in patients with chronic heart failure. Br Heart J 54: 313–320
Svenson G, Strandberg L-E, Lindvall B, Erhardt L (1988) Haemodynamic response to dopexamine hydrochloride in postinfarction heart failure: lack of tolerance after continuous infusion. Br Heart J 60: 489–496
Bristow MR, Ginsburg R, Umans V, Fowler M, Minobe W, Rasmussen R, Zera P, Menlove R, Shah P, Jamieson S, Stinson EB (1986) Beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptor subpopulations in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium: coupling of both receptor subtypes to muscle contraction and selective beta1 receptor down-regulation in heart failure. Circ Res 59: 297–309
Baumann G, Felix SB, Filcek SAL (1990) Usefulness of dopexamine hydrochloride versus dobutamine in chronic congestive heart failure and effects on hemodynamics and urine output. Am J Cardiol 65: 748–754
Smith GW, O'Connor SE (1988) An introduction to the pharmacologic properties of Dopacard (dopexamine hydrochloride). Am J Cardiol 62: 9C-17C
Leier CV, Binkley PF, Carpenter J, Randolph PH, Unverferth DV (1988) Cardiovascular pharmacology of dopexamine in low-output congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 62: 94–99
Colardyn FC, Vandenbogaerde JF, Vogelaers DP, Verbeke JH (1989) Use of dopexamine hydrochloride in patients with septic shock. Crit Care Med 17: 999–1003
Tremper KK, Shoemaker WC (1981) Transcutaneous oxygen monitoring of critically ill adults, with and without low-flow shock. Crit Care Med 9: 706–709
Mitchell PD, Smith GW, Wells E, West PA (1987) Inhibition of Uptake1 by dopexamine hydrochloride (in vitro). Br J Pharmacol 92: 265–270
Jaski BE, Peters C (1988) Inotropic, vascular and neuroendocrine effects of dopexamine hydrochloride and comparison with dobutamine. Am J Cardiol 62: 63C-67C
Drummond WH, Gregory GA, Heymann MA, Phibbs RA (1981) The independent effects of hyperventilation, tolazoline and dopamine on infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 98: 603–611
Sinner JR, Boys RJ, Hunter S, Hey EN (1992) Pulmonary and systemic arterial pressure in hyaline membrane disease. Arch Dis Child 67: 366–373
Walther FJ, Benders MJ, Leyton JO (1993) Early changes in theneonatal circulatory transition J Pediatr 123: 625–632
Hemmer M, Suter PM (1979) Treatment of cardiac and renal effects of PEEP with dopamine in patients with acute respiratory failure. Anesthesiology 40: 399–403
Mousdale S, Clyburn PA, Mackie AM, Groves ND, Rosen M (1988) Comparison of the effects of dopamine, dobutamine and dopexamine upon renal blood flow: a study in normal, healty volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 25: 555–560
Jaton T, Thonney M, Gouyon J-B, Guinard J-P (1992) Renal effects of dopamine and dopexamine in the newborn anesthetized rabbit. Life Sci 50: 195–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawczynski, P., Piotrowski, A. Circulatory and diuretic effects of dopexamine infusion in low-birth-weight infants with respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med 22, 65–70 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728334
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728334