Abstract
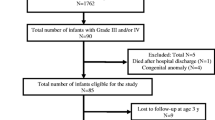
Over a 5-year period (1984–1988) intra- and periventricular hemorrhage (IVH/PVH) was observed in 299 preterm infants. Sixty-eight infants developed posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus (PH); of these, 23 infants died and 40 infants could be followed up for assessment of neurological development (5 patients were lost to follow-up). At 1 year of corrected age 15% (25% at 5 year follow-up) of the infants were determined to have developed normally, 35% (25% at 5-year follow-up) showed mild neurological symptoms and/or slight developmental delay, 32.5% (28% at 5-year follow-up) had handicaps and/or moderate mental retardation, and 17.5% (22% at 5-year follow-up) had severe handicaps and/or severe mental retardation. There was a significantly worse outcome in infants with grade 4 IVH/PVH (P<0.05) and a significantly worse outcome in the group requiring ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt (P<0.05). The results at 1 year of corrected age proved to be a quite realistic predictor of neurological functioning at 5 years of age (80% predicted correctly in the nonshunted-group — one patient lost to follow-up; 95% predicted correctly in the shunted group — four patients lost to follow-up). Cystic periventricular leukomalacia had been diagnosed in 7 (10%) patients and was associated with poor neurodevelopmental outcome. Gestational age, birth weight, time of shunt placement, and peripartum asphyxia had no significant influence on neurodevelopmental outcome. Infants with shunt infections and a high number of shunt revisions were found to have a significantly worse neurodevelopmental outcome (P<0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan WC, Dransfield DA, Tito AM (1984) Ventricular dilation following periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage: outcome at age 1 year. Pediatrics 73:158–162
Allen MC, Capute AJ (1989) Neonatal neurodevelopmental examinations as a predictor of neuromotor outcome in premature infants. Pediatrics 83:498–506
Amiel-Tison C, Grenier A (1986) Neurological assessment in the first year of life. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Amiel-Tison C, Stewart AL (1989) Follow-up studies in the first five years of life: a pervasive assessment of neurological function. Arch Dis Child 64:496–502
Arnold D, Adis B, Rettwitz W, Lasch P, Kachel W (1988) Einschäzung und therapeutische Möglichkeiten beim posthämorrhagischen Hydrocephalus des Neugeborenen. Klin Pädiatr 200:299–306
Bada HS, Salmon JH, Pearson DH (1979) Early surgical intervention in posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Child's Brain 5:109–115
Boynton BR, Boynton CA, Merrit TA, Vaucher YE, James HE, Bejar RF (1986) Ventriculoperitoneal shunts in low birth weight infants with intracranial hemorrhage: neurodevelopmental outcome. Neurosurgery 18:141–145
Brand M, Ludwig B, Voth D, Ermert JA (1983) Haben Kinder mit posthämorrhagischem Hydrocephalus eine Chance? In: Voth D, Gutjahr P, Glees P (eds) Hydrocephalus im frühen Kindesalter. Enke Stuttgart, pp 344–349
Burstein J, Papile LA, Burstein R (1979) Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in premature newborns: a prospective study with CT. Am J Radiol 132:631–635
Catto-Smith AG, Yu VYH, Bajuk B, Orgill AA, Astbury J (1985) Effect of neonatal periventricular haemorrhage on neurodevelopmental outcome. Arch Dis Child 60:8–11
Chaplin ER, Goldstein GW, Myerberg DZ, Hunt JV, Tooley WH (1980) Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in the preterm infant. Pediatrics 65:901–909
Cooke RWI (1983) Early prognosis of low birthweight infants treated for progressive posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child 58:410–414
Cooke RWI (1987) Determinants of major handicap in post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child 62:504–517
Dykes FD, Dunbar B, Lazarra A, Ahmann PA (1989) Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in high-risk preterm infants: natural history, management, and long-term outcome. J Pediatr 114:611–618
Ford L, Steichen J, Steichen PA, Babcock D, Fogelson MH (1989) Neurologic status and intracranial hemorrhage in very-low-birth-weight preterm infants. Am J Dis Child 143:1186–1190
Hale PM, McAllister JP, Katz SD, Wright LC, Lovely TJ, Miller DW, Wolfson BJ, Salotto AG, Shroff DV (1992) Improvement of cortical morphology in infantile hydrocephalic animals after ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement. Neurosurgery 31:1085–1096
Hanigan WC, Morgan AM, Anderson RJ, Bradle P, Cohen HS, Cusack TJ, Thomas-McCauley T, Miller TC (1991) Incidence and neurodevelopmental outcome of periventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in a regional population of very low birth weight infants. Neurosurgery 29:701–706
Hawgood S Spong J, Yu VYH (1984) Intraventricular hemorrhage: incidence and outcome in a population of very-low-birth-weight infants. Am J Dis Child 138:136–139
Hill A, Volpe JJ (1981) Measurement of intracranial pressure using the Ladd intracranial pressure monitor. J Pediatr 98:974–976
James HE, Boynton BR, Boynton CA, Merritt TA, Vaucher YE, Bejar RE (1987) Severe intracranial hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in low-birthweight infants treated with CSF shunts. Child's Nerv Syst 3:110–113
Kirkpatrick M, Engleman H, Minns RA (1989) Symptoms and signs of progressive hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child 64:124–128
Korobkin R (1975) The relationship between head circumference and the development of communicating hydrocephalus in infants following intraventricular hemorrhage. Pediatrics 56:74–77
Kreusser KL, Tarby TJ, Taylor D, Kovnar E, Hill A, Conry JA, Volpe JJ (1984) Rapidly progressive posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus: treatment with external ventricular drainage. AJDC 138:633–637
Krishnamoorthy KS, Shannon DC, DeLong GR, Todres ID, Davis KR (1979) Neurologic sequelae in the survivors of neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Pediatrics 64:233–237
Krishnamoorthy KS, Kuban KCK, Leviton A, Brown ER, Sullivan KF, Allred EN (1990) Periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage: sonographic localization, phenobarbital, and motor abnormalities in low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 85:1027–1033
Laurent JP, Williamson WD, Thurber SL, Cheek WR (1986) Comparison of outcome of preterm infants with and without hydrocephalus following intraventricular hemorrhage. J Pediatr Neurosci 2:116–124
Levene MI, Starte DR (1981) A longitudinal study of post-hemorrhagic ventricular dilatation in the newborn. Arch Dis Child 56:905–910
Lorber J, Bhat US (1974) Posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus: diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment and longterm results. Arch Dis Child 49:751–762
McComb JG, Ramos AD, Platzker ACG, Henderson AJ, Segall HD (1983) Management of hydrocephalus secondary to intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm infant with a subcutaneous ventricular catheter reservoir. Neurosurgery 13:295–300
Monset-Couchard M, De Bethmann O, Radvanyi MF, Moriette, Papin C, Relier JP (1987) Devenir des hémorragies péri-ventriculaires majeures à court, moyen et long terme. Arch Fr Pediatr 44:779–786
Müller WD, Urlesberger B (1992) Correlation of ventricular size and head circumference after severe intra-periventricular haemorrhage in preterm infants. Child's Nerv Syst 8:33–35
Palmer P, Dubowitz LMS, Levene MI, Dubowitz V (1982) Developmental and neurological progress of preterm infants with intraventricular haemorrhage and ventricular dilatation. Arch Dis Child 57:748–753
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H (1978) Incidence and evaluation of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage. A study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 gm. J Pediatr 92:529–534
Papile LA, Munsick-Bruno G, Schaefer A (1983) Relationship of cerebral intraventricular hemorrhage and early childhood neurologic handicaps. J Pediatr 103:273–277
Resch B, Müller W, Oberbauer R (1990) Konditionierende Faktoren für die Shuntinsuffizienz beim posthämorrhagischen Hydrocephalus des Frühgeborenen. Z Kinderchir 45:203–208
Rogers B, Msall M, Owens T, Guernsey K, Brody A, Buck G, Hudak M (1994) Cystic periventricular leucomalacia and type of cerebral palsy in preterm infants. J Pediatr 125:S1–8
Ross G, Lipper E, Auld PA (1986) Early predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome of very low-birth-weight infants at three years. Dev Med Child Neurol 28:171–179
Sasidharan P, Marquez E, Dizon E, Sridhar CV (1986) Developmental outcome of infants with severe intracranial-intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus with and without ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Child's Nerv Syst 2:149–152
Scott DT, Ment LR, Ehrenkranz RA, Warshaw JB (1984) Evidence for late developmental deficit in very low birth weight infants surviving intraventricular hemorrhage. Child's Brain 11:261–269
Shankaran S, Koepke T, Woldt E, Bedard MP, Dajani R, Eisenbrey AB (1989) Outcome after posthemorrhagic ventriculomegaly in comparison with mild hemorrhage without ventriculomegaly. J Pediatr 114:109–114
Stellmann GR, Bannister CM (1985) Factors predicting developmental outcome in premature infants with hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage. Z Kinderchir 40 [Suppl 1]: 24–26
Touwen BCL (1982) Die Untersuchung von Kindern mit geringen neurologischen Funktionsstörungen. Thieme, Stuttgart New York
Urlesberger B, Müller W, Ritschl E, Reiterer F (1991) The influence of head position on the intracranial pressure in preterm infants with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Child' Nerv Syst 7:85–87
Volpe JJ (1987) Intracranial hemorrhage: periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage of the premature infant. In: Volpe JJ (ed) Neurology of the newborn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 311–353
Volpe JJ, Herscovitch P, Perlman JM, Raichle ME (1983) Positron emission tomography in the newborn: extensive impairment of regional cerebral blood flow with intraventricular hemorrhage and hemorrhagic intracerebral involvement. Pediatrics 72:589–601
Weninger M, Salzer HR, Pollak A, Rosenkranz M, Vorkapic P, Korn A, Lesigang C (1992) External ventricular drainage for treatment of rapidly progressive posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 31:52–58
Wille L, Keller U, Dillenz M, Stenzel K (1986) Zur Frühprognose der intracraniellen Blutung bei Frühgeborenen. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 134:422–427
Wise BL, Ballard R (1976) Hydrocephalus secondary to intracranial hemorrhage in premature infants. Child's Brain 2:234–241
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Resch, B., Gerdermann, A., Maurer, U. et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome of hydrocephalus following intra-/periventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants: short- and long-term results. Child's Nerv Syst 12, 27–33 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00573851
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00573851