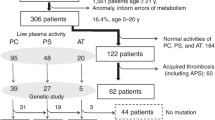
Abstract
Childhood thrombo-embolism is mostly the result of inherited thrombophilia or vascular insults combined with risk factors such as peripartal asphyxia, fetopathia diabetica, exsiccosis, septicaemia, central lines, congenital heart disease, cancer, trauma, surgery or elevated antiphospholipid antibodies. Inherited thrombophilia includes mainly defects of the protein C pathway, resistance to activated protein C, protein C or protein S deficiency. Resistance to activated protein C, in the majority of cases caused by the point mutation Arg 506 Gln of the factor V gene, has emerged as the most important hereditary cause of thrombo-embolism in adults and children. However, since an acquired risk of thrombo-embolic complications frequently masks the inherited deficiency in affected children, children with thrombo-embolism should have adequate laboratory evaluation for inherited coagulation disorders, especially the protein C pathway. Until more data on childhood thrombo-embolism are available, treatment recommendations will continue to be extrapolated from guidelines for adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APC :
-
activated protein C
- APCR :
-
resistance to the anticoagulatory effect of protein C
- aPTT :
-
activated partial thromboplastin time
- C4bB :
-
C4b binding protein
- FFP :
-
fresh frozen plasma
- PC :
-
protein C
- PS :
-
protein S
- TF :
-
tissue factor
References
Alessi MC, Aillaud MF, Paut O, Roquelaure B, Alhenc-Gelas M, Pellissier MC, Ghanen N, Juhan-Vague I (1996) Purpura fulminans in a patient homozygous for a mutation in the protein C gene — prenatal diagnosis in a subsequent pregnancy. Thromb Haemost 75:520–521
Allaart CF, Poort S, Rosendal F, Reitsma P, Bertina R (1993) Increased risk of venous thrombosis in carriers of hereditary protein C deficiency defect. Lancet 341:134–138
Amer L, Kisiel W, Searles RP, Williams RC Jr (1990) Impairment of the protein C anticoagulant pathway in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus, anticardiolipin antibodies and thrombosis. Thromb Res 57:247–258
Andrew M (1995) Developmental hemostasis: relevance to thromboembolic complications in pediatric patients. Thromb Haemost 74:415–425
Andrew M, Paes B, Milner R, Johnston M (1990) Development of the hemostatic system in the neonate and young infant. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 12:95–104
Andrew M, Vegh P, Johnston M, Bowker J, Ofosu F, Mitchell L (1992) Maturation of the hemostatic system during childhood. Blood 80:1998–2005
Andrew M, David M, Adams M (1993) Venous thromboembolic complications in children. J Pediatr 123:337–346
Arav-Bogner R, Reif S, Bujanover Y (1995) Portal vein thrombosis caused by protein C and protein S deficiency associated with cytomegalovirus infection. J Pediatr 126:586–588
Arnout J, Vanrusselt M, Vermylen J (1995) Resistance to activated protein C in a population of patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Thromb Haemost 73:1275
Auberger K (1992) Evaluation of a new protein C concentrate and comparison of protein C assays in a child with congenital protein C deficiency. Ann Hematol 64:146–151
Baliga V, Thwaites R, Tillyer ML, Minford A, Parapia L, Allgrove J (1995) Homozygous protein C deficiency — management with protein C concentrate. Eur J Pediatr 154:534–535
Bandello F, D'Angelo SV, Parlavecchia M, Tavola A, Valle PD, Brancato R, D'Angelo A (1994) Hypercoagulability and high lipoprotein (a) levels in patients with central retinal vein occlusion. Thromb Haemost 72:39–43
Bertina RM, Ploos Van Amstel HK, Wijngaarden A van, Coenen J, Leemhuis MP, Deutz Terlouw PP, Linden IK van der, Reitsma PH (1990) Heerlen polymorphism of protein S, an immunologic polymorphism due to dimorphism of residue 460. Blood 76:538–548
Bertina RM, Koeleman BPC, Koster T, Rosendaal FR, Dirven RJ, Ronde H de, Velden PA van der, Reitsma PH (1994) Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature 369:64–67
Bick RL, Baker WF (1994) The antiphospholipid and thrombosis syndromes. Med Clin North Am 78:667–684
Bick R, Ucar K (1992) Hypercoagulability and thrombosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 6:1421–1429
Bovill EG, Bauer KA, Dickermann JD, Callas P, West B (1989) The clinical spectrum of heterozygous protein C deficiency in a large New England kindred. Blood 73:712–717
Cooper PC, Hampton KK, Makris M, Abuzenadah A, Paul B, Preston FE (1994) Further evidence that activated protein C resistance can be misdiagnosed as inherited functional protein S deficiency. Br J Haematol 88:201–203
Dahlbäck B (1986) Inhibition of protein C cofactor function of human and bovine protein S by C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem 261:12022–12027
Dahlbäck B (1991) Protein S and C4b-binding protein: components involved in the regulation of the protein C anticoagulant system. Thromb Haemost 66:49–61
Dahlbäck B (1995) New molecular insights into the genetics of thrombophilia. Resistance to activated protein C caused by Arg 506 to Gln mutation in factor V as a pathogenetic risk factor. Thromb Haemost 74:139–148
Dahlbäck B (1995) Factor V gene mutation causing inherited resistance to activated protein C as a basis for venous thromboembolism. J Int Med 237:221–227
Dahlbäck B, Carlsson M (1991) Factor VIII defect associated with familial thrombophilia. Thromb Haemost 65:658
Dahlbäck B, Carlsson M, Svensson PJ (1993) Familial thrombophilia due to a previously unrecognized mechanism characterized by poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C: prediction of a cofactor to activated protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1004–1008
D'Angelo SV, Mazzola G, Valle PD, Testa S, Pattarini E, D'Angelo A (1995) Variable interference of activated protein C resistance in the measurement of protein S activity by commercial assays. Thromb Res 77:375–378
David M, Andrew M (1993) Venous thromboembolic complications in children. J Pediatr 123:337–346
David M, Manco-Johnson M, Andrew M (1995) Diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism in children and adolescents. On behalf of the subcommittee on perinatal haemostasis of the scientific and standardization committee of the ISTH. Thromb Haemost 74:791–792
Dreyfuß M, Magny JF, Bridey F, Schwarz HP, Planche C, Dehan M, Tchernia G (1991) Treatment of homozygous protein C deficiency and neonatal purpura fulminans with purified protein C concentrate. N Engl J Med 325:1565–1568
Edenbrandt CM, Lindwall A, Wydro R, Stenflo J (1990) Molecular analysis of the gene for vitamin K-dependent protein S and its pseudogene. Cloning and partial gene organization. Biochemistry 29:7861–7868
Esmon CT (1989) The role of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem 264:4743–4749
Faioni EM, Boyer-Neumann C, Franchi F, Wolf M, Meyer D, Mannucci P (1994) Another protein S functional assay is sensitive to resistance to activated protein C. Thromb Haemost 72:643–651
Foster DC, Yoshitake S, Davie EW (1985) The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4673–4677
Gandrille S, Borgel D, Eschwege-Gufflet V, Aillaud MF, Dreyfuß M, Matheron C, Gaussem P, Abgrall JF, Jude B, Sie P, Toulon P, Aiach M (1995) Identification of 15 different candidate causal point mutations and three polymorphisms in 19 patients with protein S deficiency using a scanning method for the analysis of the protein S active gene. Blood 85:130–139
Gladson CL, Scharrer I, Hach V, Beck KM, Griffin JH (1988) The frequency of type I heterozygous protein S and protein C deficiency in 141 unrelated young patients with venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 59:18–22
Göbel U (1994) Inherited or acquired disorders of blood coagulation in children with neurovascular complications. Neuropediatrics 25:4–7
Gomez E, Ledford MR, Pegelow CH, Reitsma PH, Bettina RM (1994) Homozygous protein S deficiency caused by one base pair deletion that leads to a stop codon in exon III of the protein S gene. Thromb Haemost 71:723–726
Gurewich V, Pannell R, Louie S, Kelley P, Suddith RL, Greenlee R (1984) Effective and fibrin-specific clot lysis by a zymogen precursor form of urokinase (pro-urokinase). A study in vitro and in two animal species. J Clin Invest 73:1731–1739
Hayashi T, Nishioka J, Shigekiyo T, Saito S, Suzuki K (1994) Protein S Tokushima: abnormal molecule with a substitution of Glu for Lys-155 in the second epidermal growth factor-like domain of protein S. Blood 83:683–690
Haverkate F, Samama M (1995) Familial dysfibrinogenemia and thrombophilia. Report on a study of the SSC subcommittee on fibrinogen. Thromb Haemost 73:151–161
Heijboer H, Brandjed D, Buller H, Sturk A, Wouter ten Cate J (1990) Deficiencies of coagulation inhibiting and fibrinolytic proteins in outpatients with deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med 323:1512–1516
Hirsch J (1991) Oral anticoagulant drugs. N Engl J Med 342:1865–1875
Ichinose A, Fujikawa K, Suyama T (1986) The activation of prourokinase by plasma kallikrein and ist inactivation by thrombin. J Biol Chem 261:3486–3489
Jaffe EA (1991) Endothelial structure and function. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Shattil SJ, Furie B, Cohen HJ (eds) Hematology, basic principles and practice. Churchill-Livingstone, New York, pp 1198–1213
Kluft C (1994) Constitutive synthesis of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAT-1): conditions and therapeutic targets. Fibrinolysis 8(2):1–7
Kodish E, Potter C, Kirschbaum N, Foster P (1995) Activated protein C resistance in a neonate with venous thrombosis. J Pediatr 127:645–648
Koster T, Rosendaal FR, Ronde H de, Briet E, Vandenbroucke JP, Bertina RM (1993) Venous thrombosis due to poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C: Leiden Thrombophilia Study. Lancet 342:1503–1506
Levy M, Benson L, Burrows PE, Bentur Y, Strong DK, Smith J, Johnson D, Jacobson S, Koren G (1991) Tissue plasminogen activator for the treatment of thromboembolism in infants and children. J Pediatr 118:467–472
Mahn J, Laurell M, Nilsson I, Dahlbäck B (1992) Thromboembolic disease — critical evaluation of laboratory investigation. Thromb Haemost 8:7–13
Mannucci PM, Tripodi A (1987) Laboratory screening of inherited thrombotic syndromes. Thromb Haemost 57:247–251
Marlar RA, Neumann A (1990) Neonatal purpura fulminans due to homozygous protein C or S deficiencies. Sem Thromb Hemost 16:299–309
Miletich J, Sherman L, Broze G (1987) Absence of thrombosis in subjects with heterozygous protein C deficiency. N Engl J Med 317:991–996
Müller EM, Ehrenthal W, Hafner G, Schranz D (1996) Purpura fulminans in severe congenital protein C deficiency: monitoring of treatment with protein C concentrate. Eur J Pediatr 155:20–25
Nowak-Göttl U, Schwabe D, Schneider W, Schlösser R, Kreuz W (1992) Thrombolysis with recombinant tissue type plasminogen activator in renal venous thrombosis in infancy. Lancet 340:1105
Nowak-Göttl U, Funk M, Mosch G, Wegerich B, Kornhuber B, Breddin HK (1994) Univariate tolerance regions for fibrinogen, antithrombin III, protein C, protein S, plasminogen and α2-antiplasmin in children using the new automated coagulation laboratory (ACL) method. Klin Pädiatr 206:437–439
Nowak-Göttl U, Ashka I, Koch HG, Boos J, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Deufel T, Jürgens H, Kohlhase B, Kuhn N, Laupert A, Rath B, Wolff JEA, Schneppenheim R (1995) Resistance to activated protein C (APCR) in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia — the need for a prospective multicentre study. Blood Coag Fibrinol 6:761–764
Nowak-Göttl U, Koch HG, Aschka I, Kohlhase B, Vielhaber H, Kurlemann G, Oleszuk-Rasche K, Kehl HG, Jürgens H, Schneppenheim R (1996) Resistance to activated protein C (APCR) in children with venous or arterial thromboembolism. Br J Haematol 92:992–998
Nowak-Göttl U, Kohlhase B, Vielhaber H, Aschka I, Schneppenheim R, Jürgens H (1996) APC resistance in neonates and infants: adjustment of the aPTT-based method. Thromb Res 81:665–670
Nuss R, Hys T, Manco-Johnson M (1995) Childhood thrombosis. Pediatrics 96:291–294
Petäjä J, Jalanko H, Holmberg C, Kinmmen S, Syrjälä (1995) Resistance to activated protein C as an underlying cause of recurrent venous thrombosis during relapsing nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr 127:103–105
Ploos Van Amstel HK, Zanden AL van der, Bakker E, Reitsma PH, Bettina RM (1987) Two genes homologous with human protein S cDNA are located on chromosome 3. Thromb Haemost 58:982–987
Ploos Van Amstel HK, Huisman MV, Reitsma PH, Wouter ten Cate J, Bettina RM (1989) Partial protein S gene deletion in a family with hereditary thrombophilia. Blood 73:479–483
Ploos Van Amstel HK, Reitsma PH, Bertina RM (1989) The human protein S locus: identification of the PS alpha gene as a site of liver protein S messenger RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 157:1033–1038
Ploos Van Amstel HK, Reitsma PH, Hamulyak K, Smulders CE de, Mannucci PM, Bettina RM (1989) A mutation in the protein S pseudogene is linked to protein S deficiency in a thrombophilic family. Thromb Haemost 62:897–901
Ploos Van Amstel HK, Reitsma PH, Logt CP van der, Bertina RM (1990) Intron-exon organisation of the active human protein S gene PS alpha and its pseudogene PS beta: duplication and silencing during primate evolution. Biochemistry 29:7853–7861
Plutzky J, Hoskins JA, Long GL, Crabtree GR (1986) Evolution and organization of the human protein C gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:546–550
Reitsma PH, Poort SR, Allaart CF, Briet E, Bettina RM (1991) The spectrum of genetic defects in a panel of 40 Dutch families with symptomatic protein C deficiency type I: Heterogenity and founder effects. Blood 78:890–894
Reitsma PH, Ploos Van Amstel HK, Bertina RM (1994) Three novel mutations in five unrelated subjects with hereditary protein S deficiency type I. J Clin Invest 93:486–492
Reitsma PH, Bernardi F, Doig RG, Gandrille S, Greengard JS, Ireland H, Krawczak M, Lind B, Long GL, Poort SR, Saito H, Sala N, Witt I, Cooper DN (1995) Protein C deficiency: a database of mutations, 1995 update. Thromb Haemost 73:786–879
Rodgers L, Luther C. Streptokinase therapy for deep vein thrombosis: a comprehensive review of the English literature. Am J Med 88:389–395
Rosenbaum T, Rammos S, Kniemeyer HW, Göbel U (1993) Extended deep vein and inferior vena cava thrombosis in a 15-year-old boy: successful lysis with recombinant tissue type plasminogen activator 2 weeks after onset symptoms. Eur J Pediatr 152:978–980
Ryan CA, Andrew M (1992) Failure of thrombolytic therapy in four children with extensive thrombosis. Am J Dis Child 146:187–193
Schmidel DK, Nelson RM, Broxson EH, Comp PC, Marlar RA, Long GL (1991) A 5.3-kb deletion including exon XIII of the protein S a gene occurs in two protein S-deficient families. Blood 77:551–559
Schmidt B, Andrew M (1995) Neonatal thrombosis: report of a prospective Canadian and international registry. Pediatrics 96:939–943
Schwabe D, Schlösser R, Auberger K, Kries R von, Nowak-Göttl U (1996) Thrombolyse mit rt-PA im 1. Lebensjahr. Hämostaseologie (in press)
Shen L, Dahlbäck B (1994) Factor V and protein C in degradation of factor VIIIa. J Biol Chem 269:18735–18738
Simioni P, De Ronde H, Prandoni P, Saladini M, Bertina RM, Girolami A (1995) Ischemic stroke in young patients with activated protein C resistance. A report of three cases belonging to three different kindreds. Stroke 26:885–890
Svensson PJ, Dahlbäck B (1994) Resistance to activated protein C as a basis for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med 330:517–522
Taberno M, Tomas J, Alberca I, Orfao A, Borrasca A, Vincente V (1991) Incidence and clinical characteristics of hereditary disorders associated with venous thrombosis. Am J Hematol 36:249–254
Uziel Y, Laxer RM, Blaser S, Andrew M, Schneider R, Silverman ED (1995) Cerebral vein thrombosis in childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. J Pediatr 126:722–727
Vielhaber H, Kohlhase B, Kehl HG, Fliedner M, Kececioglu D, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Kehrel B, Veltmann H, Vogt J, Nowak-Göttl U (1996) Flush heparin during cardiac catherisation prevents long-term coagulation activation in children without APC-resistance — preliminary results. Thromb Res 81:651–656
Whitlock J, Janco R, Phillips J (1989) Inherited hypercoagulable states in children. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 11:170–173
Wiman B, Hamsten A (1990) The fibrinolytic enzyme system and its role in the etiology of thromboembolic disease. Sem Thromb Haemost 16:207–214
Zenz W, Muntean W, Gallistl S, Leschnik B, Beitzke A (1994) Inherited resistance to activated protein C in a boy with multiple thromboses in early infancy. Eur J Pediatr 154:285–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowak-Göttl, U., Auberger, K., Göbel, U. et al. Inherited defects of the protein C anticoagulant system in childhood thrombo-embolism. Eur J Pediatr 155, 921–927 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02282879
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02282879