Summary
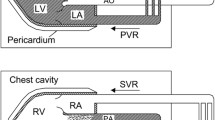
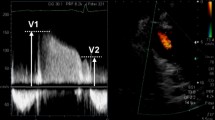
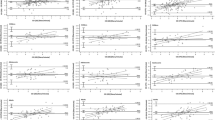
Continuous-wave Doppler echocardiography was used to estimate peak pulmonary artery (PA) pressure in 104 infants and children, aged 4 days to 16 years, with normal hearts (control group) and 43, aged 29 days to 13 years, with various kinds of heart disease (patient group). The Doppler transducer was directed toward the right ventricular outflow tract and angled until the maximal velocity signal was reached. Doppler velocity time intervals were measured as follows: acceleration time (AT), from the onset to the peak of the velocity curve; and ejection time (ET), from the onset to the termination of the velocity curve. In the control group, AT corrected through dividing by the RR interval of the electrocardiogram (ATc), and AT/ET by dividing by the square root of the RR interval (AT/ETc), were independent of body surface area. In the patient group, peak PA pressure had a significant inverse correlation with both ATc (r=-0.78) and AT/ETc (r=-0.87). Thus, AT/ETc derived from continuous-wave Doppler echocardiography is a good quantitative predictor of peak PA pressure in infants and children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirschfeld S, Meyer R, Schwartz DC, Korfhagen J, Kaplan S (1975) The echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance.Circulation 52:642–650
Isobe M, Yazaki Y, Takaku F, Koizumi K, Hara K, Tsuneyoshi H, Yamaguchi T, Machii K (1986) Prediction of pulmonary artery pressure in adults by pulsed Doppler echocardiography.Am J Cardiol 57:316–321
Kitabatake A, Inoue M, Asao M, Matsuyama T, Tanouchi J, Morita T, Mishima M, Uematsu M, Shimazu T, Hori M, Abe H (1983) Noninvasive evaluation of pulmonary hypertension by a pulsed Doppler technique.Circulation 68:302–309
Kosturakis D, Goldberg SJ, Allen HD, Loeber C (1984) Doppler echocardiographic prediction of pulmonary arterial hypertension in congenital heart disease.Am J Cardiol 53:1110–1115
Lew W, Karliner JS (1979) Assessment of pulmonary valve echogram in normal subjects and in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Br Heart J 42:147–161
Mahan G, Dabestani A, Gardin J, Allfie A, Burn C, Henry W (1983) Estimation of pulmonary artery pressure by pulsed Doppler echocardiography [abstr].Circulation [Suppl 3]68:367
Martin-Duran R, Larman M, Trugeda A, Vazquez de Prada JA, Ruano J, Torres A, Figueroa A, Pajaron A, Nistal F (1986) Comparison of Doppler-determined elevated pulmonary arterial pressure with pressure measured at cardiac catheterization.Am J Cardiol 57:859–863
Nanda NC, Gramiak R, Robinson TI, Shah PM (1974) Echocardiographic evaluation of pulmonary hypertension.Circulation 50:575–581
Okamoto M, Miyatake K, Kinoshita N, Sakakibara H, Nimura Y (1984) Analysis of blood flow in pulmonary hypertension with the pulsed Doppler flowmeter combined with cross sectional echocardiography.Br Heart J 51:407–415
Pocoski DJ, Shah PM (1978) Physiologic correlates of echocardiographic pulmonary valve motion in diastole.Circulation 58:1064–1071
Riggs T, Hirschfeld S, Borkat G, Knoke J, Liebman J (1978) Assessment of the pulmonary vascular bed by echocardiographic right ventricular systolic time intervals.Circulation 57:939–947
Serwer GA, Cougle AG, Eckerd JM, Armstrong BE (1986) Factors affecting use of the Doppler-determined time from flow onset to maximal pulmonary artery velocity for measurement of pulmonary artery pressure in children.Am J Cardiol 58:352–356
Weyman AE, Dillon JC, Feigenbaum H, Chang S (1974) Echocardiographic patterns of pulmonic valve motion with pulmonary hypertension.Circulation 50:905–910
Wilson N, Goldberg SJ, Dickinson DF, Scott O (1985) Normal intracardiac and great artery blood velocity measurements by pulsed Doppler echocardiography.Br Heart J 53:451–458
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akiba, T., Yoshikawa, M., Otaki, S. et al. Prediction of peak pulmonary artery pressure by continuous-wave Doppler echocardiography in infants and children. Pediatr Cardiol 9, 225–229 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02078413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02078413