Abstract
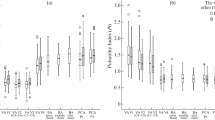
Using a colour pulsed Doppler flow mapping system, we examined the intracranial arteries of 40 healthy infants. The anterior cerebral, basilar, intracranial internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries were visualized clearly enough to evaluate flow velocity at the success rates of 100%, 87.5%, 65% and 82.4%, respectively. In the anterior cerebral, intracranial internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries, the maximum blood flow velocity slightly decreased to a minimum at around 4–6h after birth, and then gradually increased. The minimum blood flow velocity pattern was similar. The maximum blood flow velocity in the basilar artery decreased from 0–3h, rapidly increased from 4–6h, and remained at a steady level thereafter. A possible mechanism for the chronological changes in the intracranial blood flow velocity is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACA:
-
anterior cerebral artery
- BA:
-
basilar artery
- ICA:
-
intracranial internal carotid artery
- MCA:
-
middle cerebral artery
- PI:
-
pulsatility index
- VA:
-
vertebral artery
References
Archer LNJ, Evans DH, Paton JY, Levene MI (1986) Controlled hypercapnia and neonatal cerebral artery doppler ultrasound waveforms. Pediatr Res 20: 218–221
Bada HS, Hajjar W, Chu C, Sumen DS (1979) Noninvasive diagnosis of neonatal asphyxia and intraventricular hemorrhage by Doppler ultrasound. J Pediatr 95: 775–779
Deeg KH (1989) Colour flow imaging of the great intracranial arteries in infants. Neuroradiology 31: 40–43
Deeg KH, Rupprecht T (1989) Pulsed Doppler sonographic measurement of normal values for the flow velocities in the intracranial arteries of healthy newborns. Pediatr Radiology 19: 71–78
Mitchell DG, Merton D, Needleman L, Kurtz AB, Goldberg BB, Levy D, Rifkin MD, Pennell RG, Vilaro M, Baltarowich O, Dahnert W, Graziani L, Desai H (1988) Neonatal brain: color Doppler imaging. Radiology 167: 303–306
Naidich TP, Yousfzadeh DK, Gusnard DA (1986) Sonography of normal neonate head. Supratentorial structures: state-of-theart imaging. Neuroradiology 28: 408–427
Perlman JM, Hill A, Volpe JJ (1981) The effect of patent ductus arteriosus on flow velocity in the anterior cerebral arteries: ductal steal in the premature newborn infants. J Pediatr 99: 767–771
Sonessen SE, Winberg P, Lundell BPO (1987) Early postnatal changes in intracranial arterial blood flow velocities in term infants. Pediatr Res 22: 461–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, T., Ichiyama, T., Uchida, M. et al. Evaluation by colour Doppler and pulsed Doppler sonography of blood flow velocities in intracranial arteries during the early neonatal period. Eur J Pediatr 151, 461–465 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959365
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959365