Abstract
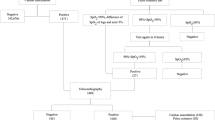
The objective of this study was to evaluate combined pulse oximetry and clinical examination as a screening method for congenital heart disease (CHD) in asymptomatic newborns. Asymptomatic newborns were screened for CHD using pulse oximetry and clinical examination before their discharge from the nursery. Oxygen saturation ≥94% was considered normal. Echocardiography was done for newborns with abnormal readings and for those with significant murmurs. Data concerning undetected cases were collected from the pediatric referral hospital. A total of 5211 cases were screened. Echocardiographic evaluations were done based on low pulse oximetry in five cases and on murmur detection in ten others. The sensitivity of the combined method of screening was 77%, whereas it was 31% for oximetry alone and 46% for clinical examination alone. Specificity was ∼100% for all methods. The positive predictive value of the combined tool was 66.7%. We conclude that combining pulse oximetry and clinical examination can enhance the clinician’s ability to detect life-threatening CHD in a timely manner. This screening method should become a part of the discharge plan for every newborn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SB Ainsworth JP Wyllie C Wren (1999) ArticleTitlePrevalence and clinical significance of cardiac murmurs in neonates Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 80 F43–45 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3lslKlsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10325811
RW Byard L Moore (1991) ArticleTitleTotal anomalous pulmonary venous drainage and sudden death in infancy Forens Sci Intl 51 197–202 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2C3M3hsFA%3D
LJ Elsas (1996) Newborn screening AM Rudolph (Eds) Rudolph’s pediatrics Appleton & Lange Stamford (CT) 282–288
V Grech (2000) ArticleTitleDiagnostic and interventional trends in tetralogy of Fallot and transposition of the great arteries in a population-based study Pediatr Cardiol 21 368–373 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvgs1Oqtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10865015
DMB Hall (Eds) (1996) Health for all children. Report of the Third Joint Working Party on Child Health Surveillance Oxford University Press Oxford
PW Hiatt L Mahony RS Tepper (1992) ArticleTitleOxygen desaturation during sleep in infants and young children with congenital heart disease J Pediatr 121 226–232 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A2cbhsVU%3D Occurrence Handle1640288
RI Koppel CM Druschel T Carter et al. (2003) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart disease in asymptomatic newborns J Pediatr 142 268–272
KS Kuehl CA Loffredo C Ferencz (1999) ArticleTitleFailure to diagnose congenital heart disease in infancy Pediatrics 103 743–747 Occurrence Handle10.1542/peds.103.4.743 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3gsFarsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10103296
RM Payne MC Johnson JW Grant AW Strauss (1995) ArticleTitleToward a molecular understanding of congenital heart disease Circulation 91 494–504 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjvVKqsLc%3D Occurrence Handle7805255
VK Reddy IR Holzman JF Wedgwood (1999) ArticleTitlePulse oximetry saturations in the first 6 hours of life in normal term infants Clin Pediatr 38 87–92 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7lslCksw%3D%3D
JD Reich S Miller B Brogdon et al. (2003) ArticleTitleThe use of pulse oximetry to detect congenital heart disease Pediatrics 111 451–455
S Richmond G Reay M Abu Harb (2002) ArticleTitleRoutine pulse oximetry in the asymptomatic newborn Arch Dis Child 87 F83–F88 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38vjsFyiuw%3D%3D
A Saxena (2003) ArticleTitleIssues in newborn screening Genet Test 7 131–134 Occurrence Handle10.1089/109065703322146812 Occurrence Handle12885334
ED Silove (1994) ArticleTitleAssessment and management of congenital heart in the newborn by the district paediatrician Arch Dis Child 70 F71–F74 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC287lvVQ%3D
S Usen M Weber K Mulholland (1999) ArticleTitleClinical predictors of hypoxaemia in Gambian children with acute lower respiratory tract infection: prospective cohort study BMJ 318 86–91 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2Fps1OgtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9880280
B Varan K Tokel G Yilmaz (1999) ArticleTitleMalnutrition and growth failure in cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease with and without pulmonary hypertension Arch Dis Child 81 49–52 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mzos1Kguw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10373135
C Wren S Richmond L Donaldson (1999) ArticleTitlePresentation of congenital heart disease in infancy: implications for routine examination Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 80 F49–F53 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3lslKlsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10325813
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakr, A., Habib, H. Combining Pulse Oximetry and Clinical Examination in Screening for Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 26, 832–835 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-005-0981-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-005-0981-9